Kepner-Tregoe Method
The Kepner-Tregoe Method was developed in the 1960s by Charles H. Kepner and Benjamin B. Kepner-Tregoe, is a structured approach for solving complex problems and making decisions. It includes situation appraisal, problem analysis, decision analysis, and potential problem analysis to improve decision quality. This method aids in addressing organisational issues and improving team collaboration.
In this blog, we will explore how to do the Kepner-Tregoe method in a step-by-step guide; we will also discuss its benefits and limitations, allowing you to decide if it's the right method for your application.
Let's jump right in…
What is The Kepner-Tregoe Method

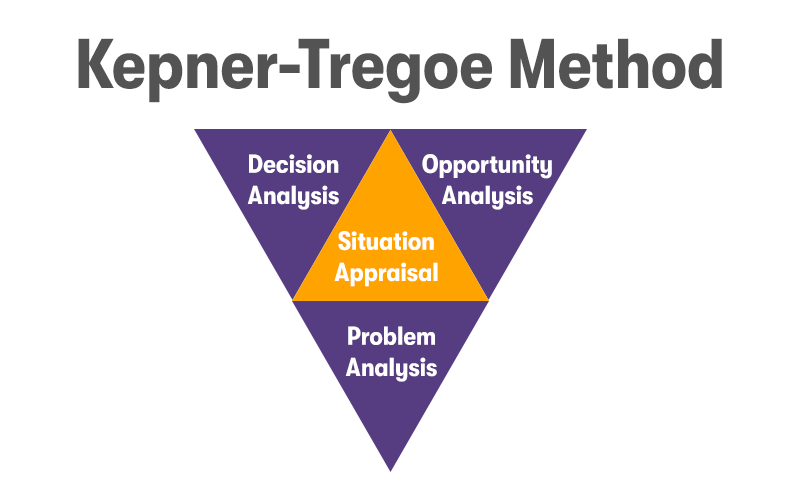
The Kepner-Tregoe Method is highly regarded in the fields of management and IT for its systematic methodology to tackle complex issues. The method emphasises a clear definition of the problem, analysis of the problem's cause, identification of possible solutions, and making and implementing decisions. The process can be broken down into four main steps:
- Situation Appraisal
- Problem Analysis
- Decision Analysis
- Potential Problem (Opportunity) Analysis
The Kepner-Tregoe Method is praised for its rational and measured approach to decision-making and problem-solving. It helps teams cut through confusion and ambiguity to get to the heart of issues quickly, making it a valuable tool in any organisational context where critical thinking is essential.
Kepner-Tregoe Problem Solving Method

The Kepner-Tregoe Problem Solving Method, also known as the Kepner-Tregoe Decision Making Method, is a systematic and structured approach for analysing and solving problems or making decisions. The method is designed to minimise bias and subjective judgment, focusing on logical and comprehensive analysis. Here is a step-by-step guide to how to do the Kepner-Tregoe Problem Solving Method:
Step 1: Situation Appraisal
The initial step, Situation Appraisal, involves taking stock of the situation to understand the scope and impact of various issues. This step is crucial for managing and prioritising a multitude of concerns that may arise in any organisational context. Key activities include:
Listing Concerns: Identify and list all current concerns, issues, or problems without trying to solve them immediately.
Clarifying Concerns: For each listed concern, gather more information to clarify the situation, ensuring a comprehensive understanding.
Setting Priorities: Determine which issues require immediate attention, which can be addressed later, and which may need further information before action can be taken. This prioritisation is often based on factors such as urgency, impact, and available resources.
Step 2: Problem Analysis
In Problem Analysis, the goal is to diagnose the root causes of the problem. This step is methodical and requires a detailed examination of the symptoms and available data:
Define the Problem: Clearly articulate what the problem is, including where and when it occurs, its magnitude, and its implications.
Collect Data: Gather relevant data that can shed light on when and where the problem occurs and under what conditions it does not. This often involves comparing 'is' (problematic) situations to 'is not' (non-problematic) situations to identify distinguishing factors.
Identify Possible Causes: Based on the data, list all potential causes that could explain the problem.
Evaluate and Test Causes: Systematically test each potential cause against the problem description and data to determine the root cause(s).
Step 3: Decision Analysis
Decision Analysis is about making the best possible choice with the information available. This involves considering various solutions or actions and assessing them against specific criteria:
Identify Objectives: Outline what the decision aims to achieve, including must-haves and nice-to-haves.
Generate Alternatives: List all possible solutions or actions that could meet the objectives.
Evaluate Alternatives: Assess each alternative against the objectives and criteria. Consider using a weighted scoring system for more complex decisions.
Make the Decision: Choose the solution that best fits the objectives and has the most favourable balance of benefits versus drawbacks.
Step 4: Potential Problem (Opportunity) Analysis
The final step, Potential Problem (Opportunity) Analysis, involves preparing for the implementation of the decision. This means anticipating possible challenges and opportunities that could emerge as a result:
Identify Potential Problems: Consider what could go wrong with the chosen solution, including new problems that might arise and existing problems that could worsen.
Plan Preventive Measures: Develop strategies to prevent identified potential problems or to mitigate their impact should they occur.
Prepare Contingency Plans: For problems that cannot be prevented, prepare contingency plans to address them effectively if they happen.
Kepner-Tregoe Matrix
The Kepner-Tregoe Matrix provides a structured framework that helps individuals and organisations evaluate their options logically and systematically, minimising the influence of bias and emotion in the decision-making process. This matrix is particularly useful in complex scenarios where multiple factors must be considered and there is no obvious choice. Here's how the Kepner-Tregoe Matrix works in more detail:
Setting Up the Matrix
Identify Decision Criteria: First, list all the criteria that are important for making the decision. These criteria are the factors that will influence the decision, such as cost, efficiency, effectiveness, and impact on stakeholders.
Weight the Criteria: Assign a weight to each criterion based on its importance. The weights help to prioritise certain factors over others in the decision-making process. The weighting can be on a scale of 1 to 10, where 10 represents the highest importance.
List the Alternatives: Identify the possible alternatives or options that are being considered as solutions to the problem.
Evaluating Alternatives
Rate Each Alternative: Evaluate how well each alternative meets each criterion. This is usually done using a numerical scale (for example, 1 to 10), where higher numbers indicate a better match to the criterion.
Calculate Weighted Scores: Multiply the rating for each alternative against each criterion by the weight of that criterion. This yields the weighted scores.
Sum the Scores: Add up the weighted scores for each alternative across all criteria to get a total score for each option.
Making the Decision
Analyse the Results: The alternative with the highest total score is typically considered the best option based on the predefined criteria and weights. However, it's essential to review the results critically, considering any assumptions or biases that might have influenced the scoring.
Consider Intangibles: Sometimes, there might be intangible factors not captured in the matrix that could influence the decision. It's important to consider these aspects before finalising the choice.
Make the Decision: Based on the matrix analysis and consideration of any intangibles, make the informed decision.
The Kepner-Tregoe Matrix is not just about identifying the "best" choice in absolute terms but rather about making a decision that best fits the specific goals, priorities, and constraints of the situation. It encourages thoroughness in considering how each option measures up against critical success factors, making it a valuable tool for complex decision-making scenarios.
The Benefits of Kepner-Tregoe Method

The Kepner-Tregoe Method offers several benefits for problem-solving and decision-making, particularly in complex and high-stakes environments. By providing a structured framework, it helps individuals and organisations make more rational, informed, and effective choices. Here are some of the key benefits of the Kepner-Tregoe Method:
Structured Approach to Problem-Solving
It offers a systematic process for identifying and solving problems, reducing the likelihood of oversight and error.
The methodical approach ensures that all aspects of a problem are considered, including potential causes and effects.
Improved Decision Making
By comparing options against a set of defined criteria, decisions are more likely to be objective and aligned with organisational goals.
The process minimises bias and emotional influence, leading to more rational and balanced decisions.
Enhanced Problem Analysis
The method encourages a deep understanding of the problem by distinguishing between symptoms and root causes.
It facilitates the identification of the real issues to be addressed, which can prevent recurring problems.
Efficient Use of Resources
Prioritising issues and focusing on the most critical problems first can lead to a more efficient allocation of time, effort, and resources.
By avoiding unnecessary actions on less critical issues, organisations can achieve better outcomes with the same or fewer resources.
Better Risk Management
The Potential Problem Analysis step helps in anticipating possible future problems, allowing for the development of preventive measures and contingency plans.
This proactive approach to risk can save time and resources by avoiding or mitigating future crises.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
The clear, step-by-step process facilitates better communication and collaboration within teams.
It provides a common language and framework for discussing problems and decisions, making it easier to build consensus and commitment to the chosen course of action.
Flexibility and Applicability
The Kepner-Tregoe Method is versatile and can be applied to a wide range of problems and decisions, across different industries and organisational functions.
Its principles are adaptable to both small-scale and large-scale issues.
Increased Confidence in Outcomes
By thoroughly analysing problems and evaluating decisions, individuals and organisations can have greater confidence in the outcomes of their actions.
This confidence can lead to more decisive action and the willingness to tackle complex challenges.
Development of Critical Thinking Skills
Regular use of the Kepner-Tregoe Method can help in developing and honing critical thinking skills among team members.
These skills are transferable and can improve overall organisational capability in problem-solving and decision-making.
The Limitations of Kepner-Tregoe Method

While the Kepner-Tregoe Method is highly effective for structured problem-solving and decision-making, it does have some limitations that may affect its applicability or effectiveness in certain scenarios. Understanding these limitations is crucial for organisations aiming to implement this method effectively. Here are some of the key limitations:
Complexity and Time Consumption
The structured and detailed approach, while thorough, can be complex and time-consuming, especially for straightforward problems where quick decisions are needed.
This might lead to delays in decision-making or problem-solving in fast-paced environments.
Training and Skill Requirements
Effective application of the Kepner-Tregoe Method requires proper understanding and training. Organisations might need to invest in training their staff, which can be resource-intensive.
Without adequate training, there's a risk of incorrect application, which can undermine the effectiveness of the process.
Possible Over-Reliance on Process
Users may become overly reliant on the method, applying it rigidly even when a more flexible approach could be more appropriate.
Over-reliance on the structured process might stifle creativity and innovation in problem-solving.
Potential for Bias in Criteria and Weighting
While the method aims to minimise bias, selecting and weighing criteria in the decision-making process can still introduce subjectivity, potentially skewing outcomes.
The effectiveness of the decision analysis depends on the objectivity and accuracy of these initial inputs.
Difficulty with Intangible Factors
The method primarily focuses on quantifiable data and may not adequately capture intangible factors, such as employee morale, brand reputation, or cultural impacts, which can be crucial in some decisions.
This limitation might lead to underestimating the importance of these factors in the decision-making process.
Adaptability Issues
In environments where conditions change rapidly, the static nature of the initial analysis might become quickly outdated, requiring constant re-evaluation and adjustment.
The method might not be as effective in highly dynamic or uncertain environments where flexibility and adaptability are key.
Resource Intensiveness for Small Decisions
Applying the Kepner-Tregoe Method to minor or routine decisions might not be cost-effective due to its resource-intensive nature.
Organisations need to balance the depth of analysis with the scale of the decision to ensure efficient use of resources.
Potential for Overlooked Alternatives
The focus on analysing identified alternatives might result in missing out on innovative or unconventional solutions that fall outside the initial set of options considered.
There's a need for openness to revisiting the problem definition and potential solutions periodically.
Despite these limitations, the Kepner-Tregoe Method remains a powerful tool for systematic problem-solving and decision-making. By being aware of its limitations and applying the method judiciously, organisations can maximise its benefits while mitigating potential downsides.
Where to Learn More About Problem Management and Root Cause Analysis?
Our Problem Management & Root Cause Analysis Techniques Workshop will teach you which techniques are most useful for different types of problems and when it's appropriate to undertake root cause analysis. You will also identify barriers to effective problem solving and how to overcome them and information gathering techniques.
Click here to learn more about Root Cause Analysis.
Final Notes on Kepner Tregoe Method
In conclusion, the Kepner-Tregoe Method provides a systematic way to solve problems and make decisions in organisations, covering steps from situation appraisal to potential problem analysis. It helps individuals and teams methodically tackle complex challenges, offering benefits like better decision-making and risk management.
However, it has drawbacks, such as complexity and the need for extensive training. Applying the method requires balancing its structure with the dynamic nature of organisations. Recognising its strengths and weaknesses allows for its effective use, leading to informed and rational decisions.
For one last tip, continuously practice and reflect on the Kepner-Tregoe Method. Review past decisions to refine your approach and enhance future problem-solving effectiveness. Mastery evolves with experience and thoughtful application.